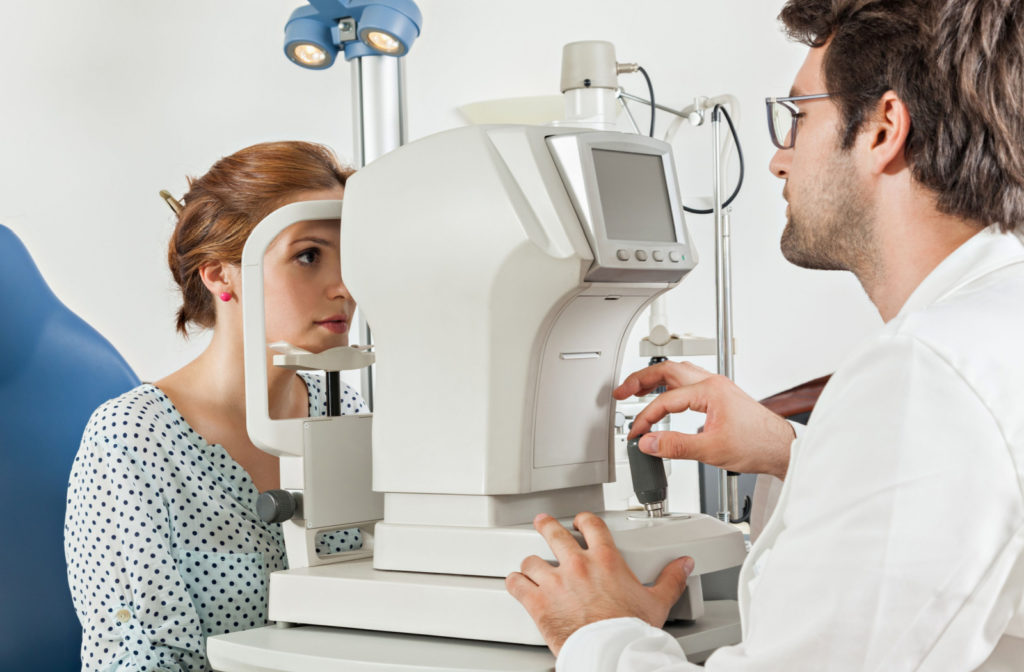
A retinal exam is a crucial part of a comprehensive eye exam. This exam assesses your vision and eye health using a series of tests, and a retinal scan lets your eye doctor see the details of the back of your eyes.
The retina is a light-sensitive layer of cells on the back of your eye that receives images and sends them to the brain—this is how you see.
Regular eye checkups are essential for protecting your eyes and preventing eye and health problems in their early stages.
According to the World Health Organization, 80% of all cases of blindness are preventable. Skipping your comprehensive eye exam or important tests like retinal scans means you may miss crucial signs of an eye condition.
What Is Dilation?
To get a clearer view of the interior of your eye, your optometrist may dilate your pupils. This process involves putting drops into your eyes, allowing for clear visibility of blood vessels and the optic nerve.
This process can also help your optometrist identify other health conditions that may not seem related to the eyes, such as hypertension, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis (MS).
The muscle responsible for controlling pupil dilation is called the iris dilator muscle. This muscle is made up of fibers arranged radially and connects the exterior of the iris to the interior. Contraction of the dilator muscle pulls the interior of the iris outward, resulting in an increase in the size of the pupil.
Eye drops such as tropicamide and phenylephrine are specifically designed to enlarge the pupils of your eyes. The mechanism behind tropicamide relaxes a particular muscle in the eye, while phenylephrine contracts another muscle.
Patients who use tropicamide typically experience its effects in about 25 to 30 minutes and can last up to 8 hours. However, in some cases, the effects may take up to 24 hours to wear off.

What Are the Downsides of Dilation?
Eye dilation drops can cause a range of side effects. One of the most immediate is a stinging sensation when they make contact with the eyes. To alleviate this sensation, doctors may apply numbing drops before the dilation drops.
Once the dilation drops take effect, you may experience blurred vision, difficulty focusing on nearby objects, and sensitivity to light. These side effects typically last for several hours.
Rarely, an allergic reaction may occur, resulting in red and swollen eyes. Severe allergic reactions can also produce symptoms such as dry mouth, facial flushing, fever, and rapid pulse.
If you experience these symptoms after receiving eye dilation drops, seek medical attention immediately.
What Is Optomap Retinal Imaging?
Optomap retinal imaging is a revolutionary tool that can detect a wide range of conditions that eventually lead to vision impairment or blindness.
Optomap is a digital image of the retina produced by Optos scanning laser technology. It’s the only technology that can capture 82% of your retina at one time. With its ultra-widefield view, optomap enables eye care practitioners to detect early signs of retinal disease.
Optomap images are created using non-invasive, low-intensity scanning lasers. No adverse health effects have been reported in over 150 million sessions, meaning it’s safe for every family member. Optomap can save images of your eyes for future comparisons, making it easier for your eye care specialist to spot potential issues down the road.
Early detection is important for protecting your eye health. It can help ensure successful treatments are administered, ultimately reducing the risk to your sight and overall health.
What Are the Downsides Of Optomap Retinal Imaging?
There are some disadvantages of Optomap:
- Vision insurance may not always cover the cost of the required imaging.
- Not all providers offer this service.
- Even if an issue is detected through imaging, further investigation through dilation may still be necessary.
- Certain conditions, like glaucoma, require dilation for accurate diagnosis, despite the potential benefits of Optomap imaging.
- Some cases of retinal detachment have been falsely identified through Optomap imaging.
Which Reigns Supreme?
Dilation is still the most effective method to get a complete view of the inner eye. With dilation, your optometrist can observe up to 240 degrees of the eye, while optomap only shows 200 degrees.
Optomap is a fantastic technology, and it’s now often used with dilation. Having images of the inner eye is beneficial for comparison’s sake, and it’s quick and non-invasive.
If you want the best examination of the inner eye, choose dilation. The extra 40-degree view may show signs of optic nerve damage, diabetes, and macular degeneration that the Optomap can miss.
Optomap retinal imaging is not a substitution for dilation. Still, it is a fantastic tool for comparing the eye year after year. Call us today at Total Vision Del Mar to book your eye exam and see what retinal imaging can show us.